The Income Summary balance is ultimately closed to the capital account. Now for this step, we need to get the balance of the Income Summary account. In step 1, we credited it for $9,850 and debited it in step 2 for $8,790. Let’s look at a few commonly asked questions regarding temporary accounts.
Temporary Accounts in Accounting: Final Thoughts

The bottom line of these accounts is net profit (or loss) at the end of each accounting period. Once this amount is carried forward to the balance sheet, the ending balances of all temporary accounts become nil. Since revenue accounts are natural credit accounts, in order to close a revenue account at the end of a financial year, a debit entry needs to be created with the balance of the revenue accounts. The other side of the entry (credit) goes to the income summary account. This alignment is crucial because it affects the timing of tax deductions and the recognition of income, which can have a substantial impact on the amount of tax owed.
Understanding Depreciation: A Comprehensive Guide for Financial Professionals
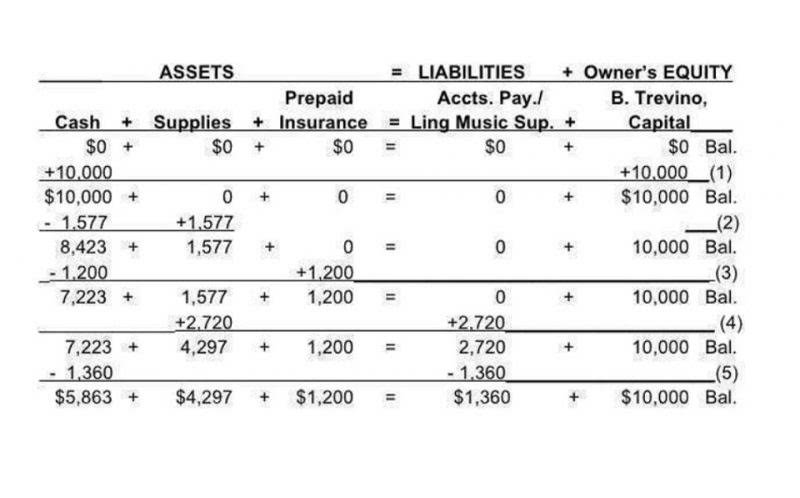
All drawing accounts are closed to the respective capital accounts at the end of the accounting period. Temporary accounts include all revenue and expense accounts, and also withdrawal accounts of owner/s in the case of sole proprietorships and partnerships (dividends for corporations). Temporary accounts include all revenue What is bookkeeping accounts, expense accounts, and in the case of sole proprietorships and partnerships, drawing or withdrawal accounts.
- In step 1, we credited it for $9,850 and debited it in step 2 for $8,790.
- Once this amount is carried forward to the balance sheet, the ending balances of all temporary accounts become nil.
- Temporary accounts, also known as nominal accounts, refer to accounts closed at the end of each accounting period.
- Ensuring temporary accounts start a new financial year with a zero balance should become second nature.
- Rather, a drawing account is a capital account as when you debit a drawing account, the corresponding credit goes to a capital account.
- The Income Summary balance is ultimately closed to the capital account.
For corporations:
- Temporary accounts refer to accounts that are closed at the end of every accounting period.
- Taking the example above, total revenues of $20,000 minus total expenses of $5,000 gives a net income of $15,000 as reflected in the income summary.
- All temporary accounts eventually get closed to retained earnings and are presented on the balance sheet.
- It can be a calendar year for one business while another business might use a fiscal quarter.
- Permanent accounts, found on the balance sheet, include assets, liabilities, and equity accounts.
More specifically, temporary accounts keep the record of transactions for a financial period. Expenses are an important part of any business because they keep the company going. The expense accounts are temporary accounts that show everything that the company spent on its operations, including advertising and supplies, among other expenses.
Types of Permanent Accounts
- As you will see later, Income Summary is eventually closed to capital.
- A drawings account is otherwise known as a corporation’s dividend account, the amount of money to be distributed to its owners.
- This alignment is crucial because it affects the timing of tax deductions and the recognition of income, which can have a substantial impact on the amount of tax owed.
- For example, during an accounting period, all revenue transactions are recorded in the revenue accounts.
- Net income is the portion of gross income that’s left over after all expenses have been met.
When preparing taxes, temporary accounts take on a significant role, as they are the primary source for reporting a company’s taxable income. Throughout the fiscal year, these accounts accumulate transactions that will ultimately influence the tax liability of a business. Revenue and expense accounts, in particular, are scrutinized to determine the net income, which forms the basis of income tax calculations.
- These figures are essential for businesses to gauge their performance and inform decision-making.
- This transfer is achieved through journal entries that credit revenue accounts and debit expense accounts, with the net difference adjusted against the retained earnings or capital accounts.
- On the balance sheet, $75 of cash held today is still valued at $75 next year, even if it is not spent.
- Once the year-end processing has been completed, all of the temporary accounts have been emptied and therefore “closed” for the current fiscal year.
- At the end of a financial period, all transactions from the revenue accounts and expense accounts are transferred to the income summary account as shown above.
- They allow for transactions to be reflected correctly in the right financial period as long as they are accurately closed out at the end of every financial period.
Closing Entry: What It Is and How to Record One
Permanent accounts represent the performance of an entity for the life of an entity. Revenue accounts are any accounts used to record sale transactions or any other types of income for a company, such as dividend income, interest income or gains on sale of assets just to name a few. The closing process is not only a matter of routine law firm chart of accounts bookkeeping but also a strategic review point. It provides an opportunity for accountants to verify the accuracy of recorded transactions and make necessary adjustments.

A business records all transactions on the general ledger as and when they happen. The title of a temporary account remains the same for the next accounting period. However, its ending balance is carried forward to permanent accounts on the balance sheet at the end of each accounting cycle. These accounts can be split into three categories; what do the balances of temporary accounts show? the revenue accounts, the expense accounts and the income summary accounts. Permanent accounts, found on the balance sheet, include assets, liabilities, and equity accounts. These accounts provide a cumulative record of a company’s financial history and are not reset at the end of the accounting period.
Accounting Crash Courses

A drawings or dividends account shows the cumulative amount withdrawn by the owner of a business during the accounting period. Each temporary account begins with a zero balance and the ending balance is transferred to the balance sheet. As both these accounts are temporary, ABC will move the ending balances to the income statement. Let us discuss what is a temporary account, its different types, and its key differences from a permanent account.